חיישן בעירה קטליטית (חיישן בשיטת הבעירה הקטליטית) הוא אחד מחיישני הגז הנפוצים ביותר, שתוכנן במיוחד לזיהוי של גזים דליקים שונים. עיקרון פעולתו מבוסס על החום שנוצר כאשר גזים דליקים בוערים על גבי קטליזטור חמצון. סוג זה של חיישן מציע קצב תגובה גבוה, ו Sobav ברגישות, דיוק וחזרתיות.
כאשר החיישן מופעל, הסליל המתכתי יקר הערך שבפנים מחמם את אלמנט הזיהוי לטמפרטורות בין 300°C ל-450°C. גזים דליקים שנשרפים על פני שטח אלמנט הזיהוי מעלים את הטמפרטורה שלו, מה שמגדיל את ההתנגדות של הסליל המתכתי יקר הערך. שינוי בהתנגדות עומד כמעט ביחס ישר לריכוז הגז. מעגל גשר בתוך החיישן זיהה את שינוי ההתנגדות וממיר אותו לפלט מתח, ובכך קובע את ריכוז הגז.
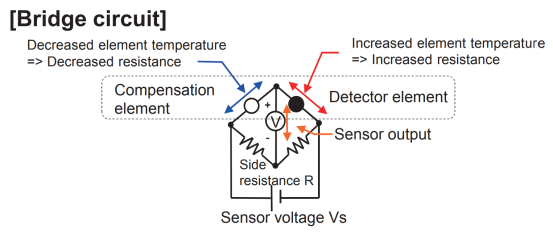
החיישן מגיב לכל הגזים הניתנים לדלק, מה שהופך אותו לא מתאים לזיהוי ריכוז של גז ספציפי בסביבות מורכבות של גזים דליקים.
בגלל עיקרון הפעולה שלו שמבוסס על בעירה, כאשר ריכוז הגז הניתן לדלק גבוה מדי, עלול להתרחש בעירה לא שלמה, מה שעלול לגרום להצטברות פחמן על אלמנט ההשראה. זה מפחית בצורה משמעותית הן את דיוק ההשראה והן את אורך החיים של הסנсор. לכן, יש לשלב מנגנון הגנה במעגל החיצוני במהלך השימוש: כאשר ריכוז הגז מגיע ל-100% LEL, יש לנתק את אספקת החשמל לסנсор כדי למנוע נזק.
 חדשות חמות
חדשות חמות2025-11-21
2025-11-13
2025-11-13
2025-10-29
2025-10-22
2025-10-28